BGP, or Border Gateway Protocol, is a crucial element in the world of computer networks, responsible for facilitating the exchange of routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS). Within BGP, two distinct protocols play pivotal roles: Internal BGP (iBGP) and External BGP (eBGP). Understanding the differences between iBGP and eBGP is essential for network administrators and engineers to make informed decisions about routing configurations.
What is BGP?
At its core, BGP in computer networks is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information between different ASes on the internet. Unlike interior gateway protocols that operate within a single AS, BGP manages the connections between ASes, making it a vital component for internet routing.
iBGP vs. eBGP: Understanding the Basics
Differentiating between Internal BGP (iBGP) and External BGP (eBGP)
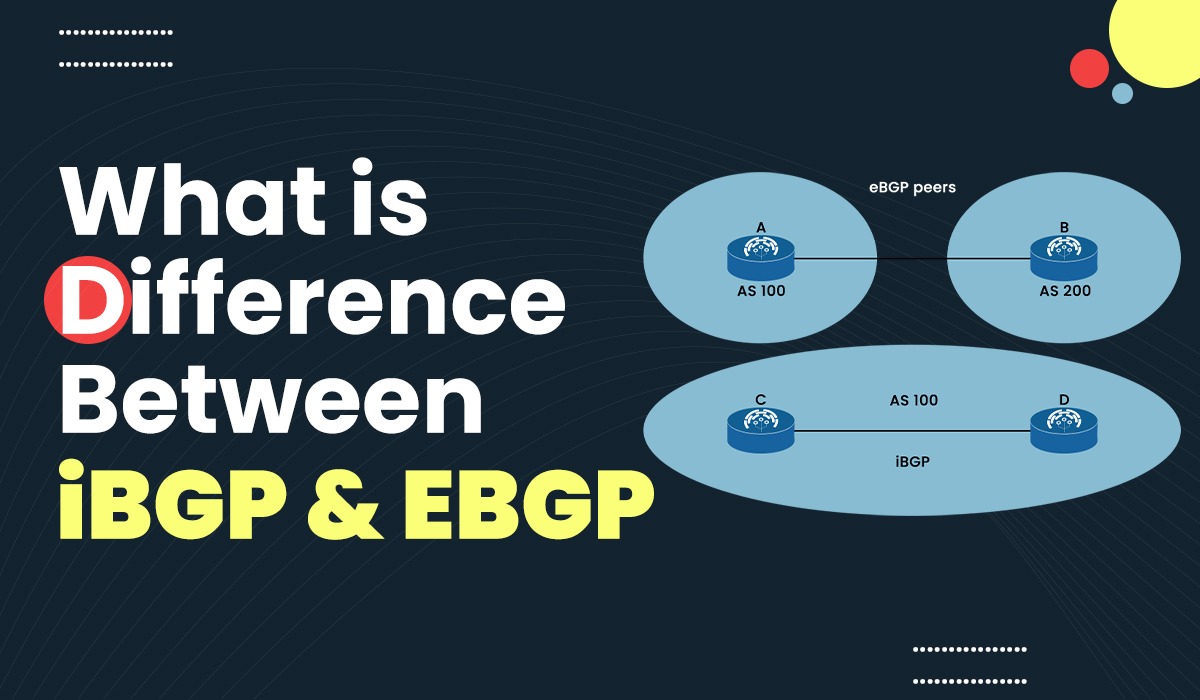
iBGP and eBGP serve distinct purposes within the realm of BGP. iBGP operates within a single AS, facilitating communication between routers within the same autonomous system. On the other hand, eBGP manages communication between routers in different ASes, playing a crucial role in interconnecting separate networks.
Key Distinctions in Their Applications
The primary difference lies in their applications. iBGP is utilized for internal routing within an organization, ensuring efficient communication between routers within the same AS. In contrast, eBGP is employed for external communication, enabling routers from different ASes to exchange routing information.
iBGP in Detail
- Internal BGP Explained
iBGP is designed to maintain consistent and accurate routing information within an AS. Routers running iBGP share routing updates, allowing them to make informed decisions about the best path to reach a particular destination within the same AS.
- Use Cases and Scenarios Where iBGP is Applied
iBGP finds its application in scenarios where routers within an AS need to exchange routing information without relying on external sources. For example, in large enterprises with complex network architectures, iBGP ensures seamless communication between internal routers.
eBGP in Detail
- External BGP Explained
In contrast, eBGP is concerned with the exchange of routing information between routers in different ASes. This external communication is vital for the global connectivity of the internet, enabling networks to discover optimal paths to reach destinations beyond their own AS.
- Real-world Applications and Significance
eBGP is crucial for internet service providers (ISPs) and large organizations that connect to multiple external networks. By exchanging routing information with routers in other ASes, eBGP enables the creation of a comprehensive and efficient routing infrastructure.
iBGP vs eBGP: Protocol Variations
- Differences in the Way iBGP and eBGP Operate
While both iBGP and eBGP operate based on the BGP protocol, there are notable differences in their behavior. iBGP vs eBGP, being internal, is more concerned with maintaining consistency within the AS, whereas eBGP focuses on the exchange of information across AS boundaries.
- Protocol Specifications and Standards
The specifications and standards for iBGP and eBGP are defined in RFC 4271. However, the application of these protocols varies based on the specific requirements of internal or external routing.
Routing Information Exchange
- How iBGP Handles Routing Information Within an Autonomous System (AS)
iBGP routers within the same AS exchange routing information to ensure that each router has a consistent view of the network. This internal communication is crucial for making efficient routing decisions based on the most up-to-date information.
- eBGP’s Role in Exchanging Routing Information Between Different ASes
eBGP, on the other hand, is responsible for exchanging routing information between routers in different ASes. This external communication is vital for ensuring that each AS is aware of the best paths to reach destinations outside its own network.
Administrative Boundaries and Attributes
- Exploring the Administrative Boundaries in iBGP
In iBGP, routers within the same AS are considered peers, and the administrative boundaries are limited to the confines of the organization. This internal nature simplifies certain aspects of routing but requires careful configuration to avoid inconsistencies.
- Attributes Specific to eBGP and Their Impact on Routing Decisions
eBGP, dealing with external connections, introduces administrative boundaries between different organizations. Additionally, eBGP routers exchange various attributes that influence routing decisions, such as the AS path, next hop, and multi-exit discriminators.
Path Selection Criteria
- Examining the Criteria for Path Selection in iBGP
iBGP routers use a set of criteria to select the best path to a destination within the same AS. These criteria include the length of the AS path, the next hop, and various BGP attributes.
- Understanding How eBGP Determines the Best Path
eBGP routers, dealing with external paths, consider factors like the shortest AS path, the next hop, and various policy-based attributes to determine the best path for routing.
Scalability Considerations
- Challenges and Solutions Related to iBGP Scalability
iBGP scalability can be a challenge in large networks. Careful design, route reflection, and confederation are common solutions to address the scalability issues associated with iBGP.
- eBGP’s Scalability Advantages and Limitations
eBGP, due to its external focus, often enjoys better scalability. However, managing a large number of eBGP peers requires careful planning and configuration to avoid performance issues.
iBGP Security Features
Security in iBGP is crucial for maintaining the integrity of internal routing information. Measures such as authentication, message integrity, and session encryption contribute to a secure iBGP environment.
- eBGP Security Considerations and Best Practices
eBGP, being involved in external communications, requires additional security measures. Implementing mechanisms like prefix filtering, route validation, and the use of BGP communities can enhance the security of eBGP connections.
Operational Differences
- Operational Aspects That Distinguish iBGP from eBGP
iBGP’s focus on internal routing simplifies certain operational aspects but requires careful consideration of route reflectors or confederation in large networks. eBGP, with its external connections, demands attention to diverse peering relationships and potential policy conflicts.
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Understanding common issues in iBGP and eBGP is essential for efficient troubleshooting. Whether it’s a synchronization problem in iBGP or route advertisement issues in eBGP, having troubleshooting strategies in place is crucial.
Best Practices for Implementation
Recommendations for Effectively Deploying iBGP
- Properly configure route reflectors or consider the use of confederation for large iBGP deployments.
- Regularly monitor and maintain the iBGP network to ensure consistency and optimal routing.
Best Practices for Optimizing eBGP Configurations
- Implement prefix filtering to control the advertisement of routes.
- Use BGP communities strategically to influence routing decisions in eBGP.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When should I use iBGP in my network?
- A: iBGP is ideal for internal routing within an autonomous system, especially in large enterprises with multiple locations.
What are the security considerations for eBGP connections?
- A: Implement prefix filtering, route validation, and BGP communities to enhance the security of eBGP connections.
How does eBGP contribute to internet connectivity?
- A: eBGP enables routers from different autonomous systems to exchange routing information, contributing to the global connectivity of the internet.
What are the scalability challenges associated with iBGP?
- A: iBGP scalability challenges can be addressed through careful design, route reflection, and the use of confederation in large networks.
How can I optimize eBGP configurations for better routing control?
- A: Implement prefix filtering and strategically use BGP communities to influence routing decisions in eBGP configurations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the distinction between iBGP and eBGP is pivotal for anyone dealing with BGP in computer networks. While iBGP focuses on internal communication within an AS, eBGP manages the exchange of information between different ASes. Choosing the right protocol depends on the specific requirements of the network, and understanding their differences is key to effective BGP implementation.